Equipment for characterisation at the a/w interface
Langmuir-Pockels surface balances
These troughs allow us to obtain spread (Langmuir) and adsorbed (Gibbs) monolayers, as well as tensiometry measurements, and therefore the determination of cmc values.
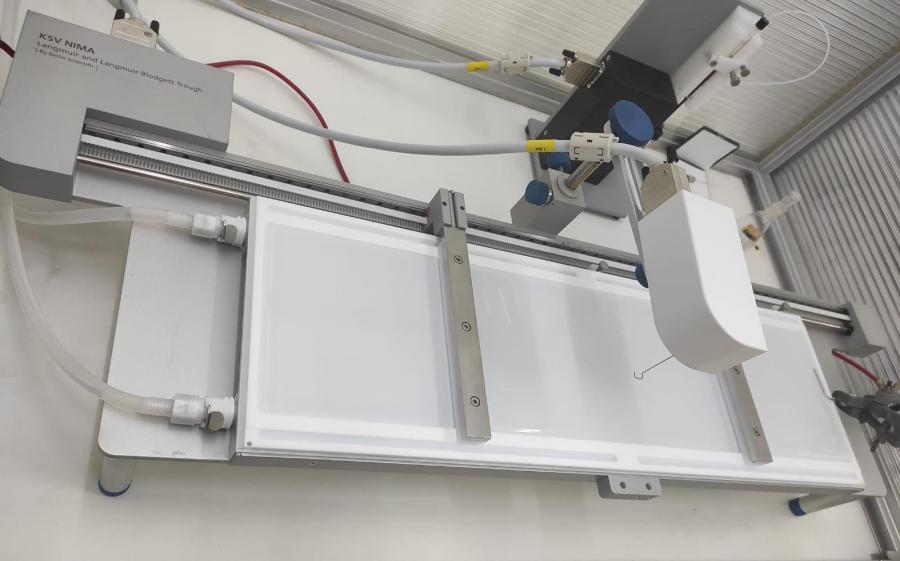
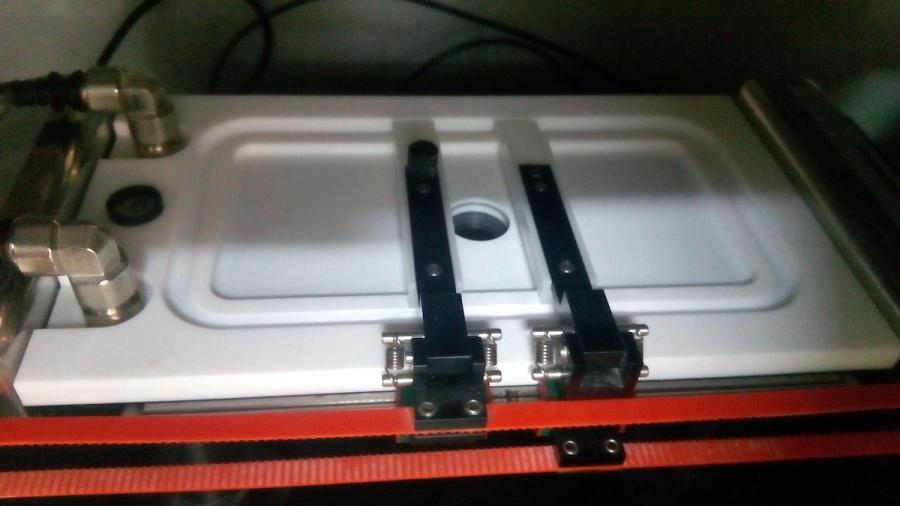



Langmuir-Blodgett surface balances
To obtain monolayers either on an aqueous or a solid (Langmuir-Blodgett e Langmuir-Schaeffer) substrate, apt for further characterisation.
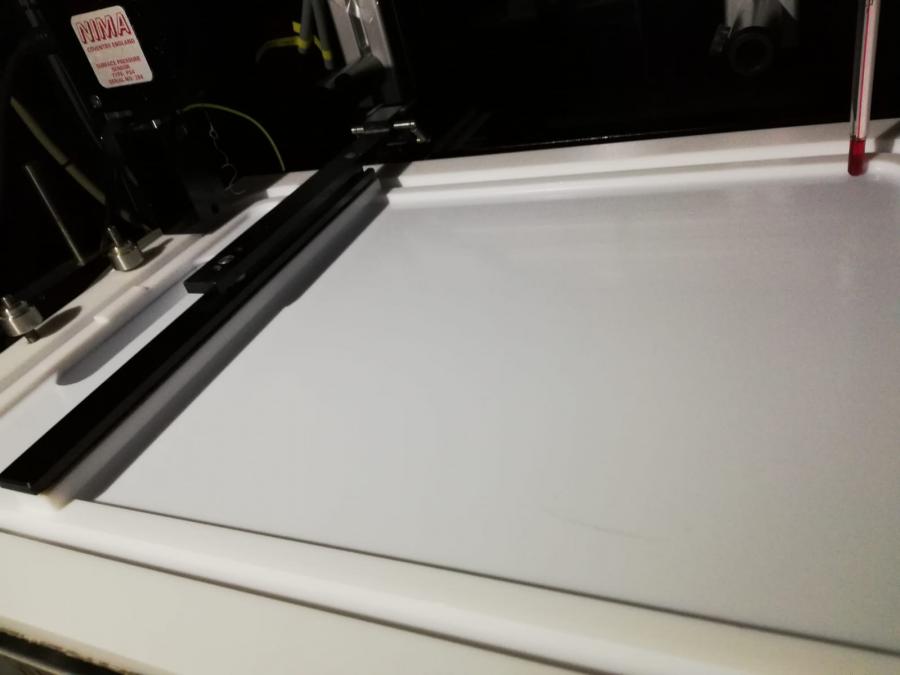
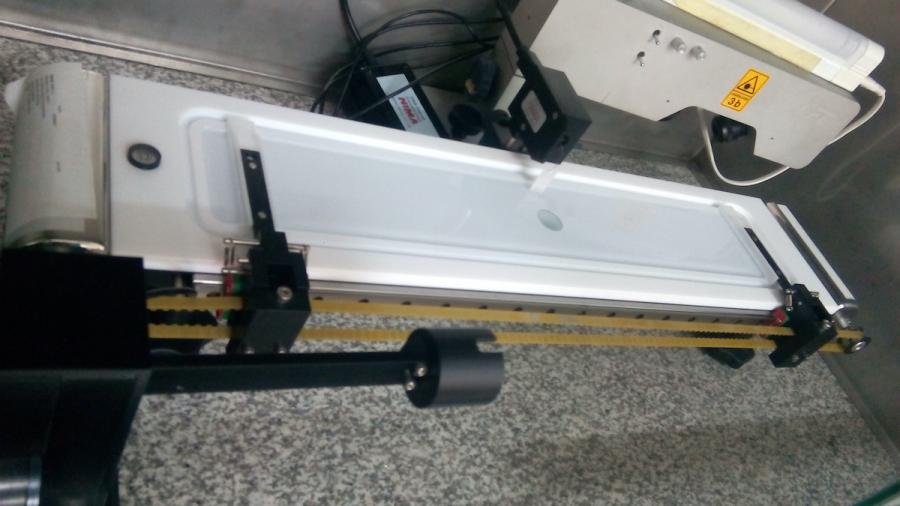


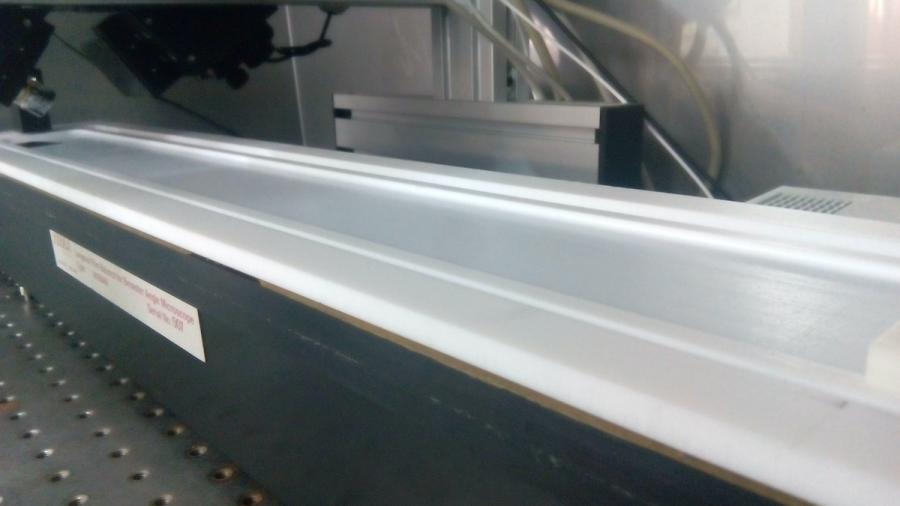
Penetration trough
The penetration trough allows us to measure adsorption kinetics of water-insoluble drugs onto membranes and their penetation into them. This technique provides useful information at the molecular scale on possible mechanisms of action of drugs at the plasma membrane as well as on systemic absorption of active ingredients, mediated by diffusion across lipid membranes.
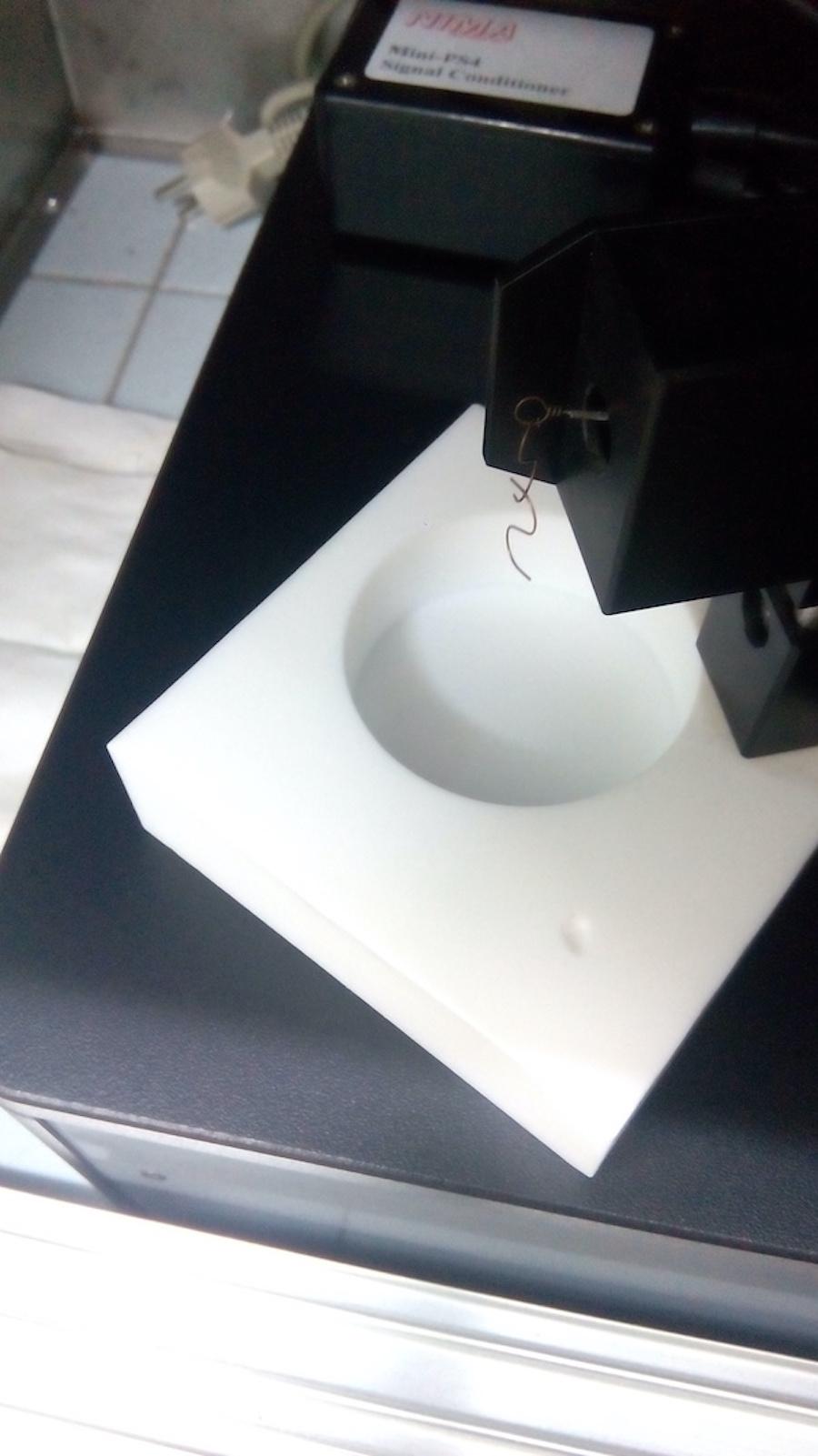

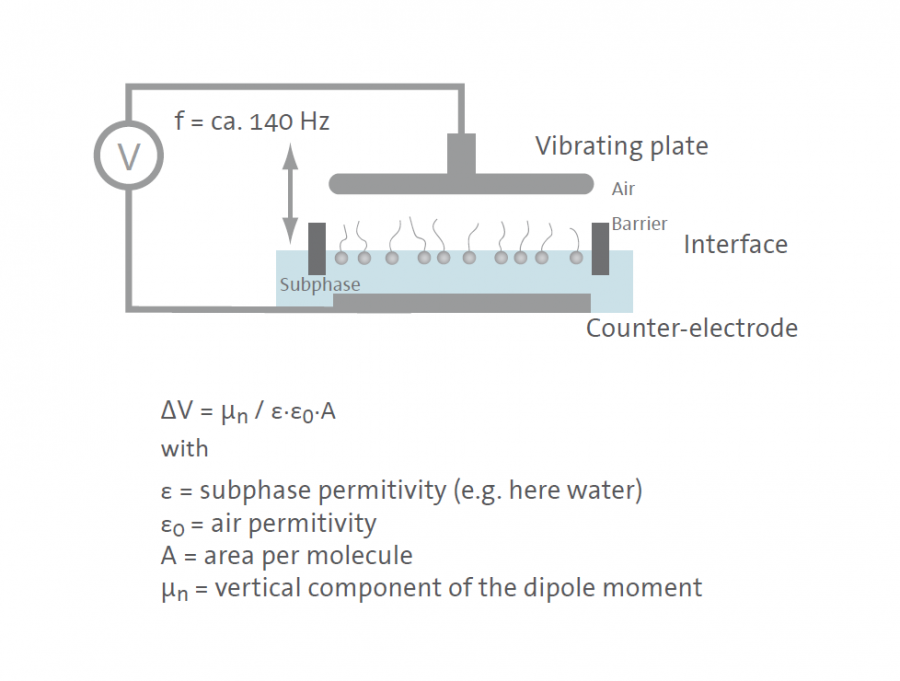
Surface potential
Surface potential measurements inform on the orientation of dipoles at interfaces, since the value of the component normal to the interface is related to the difference of electric potential measured between both electrodes. We apply this technique to obtain valuable information on the orientation of lipids and other surfactants in biomembranes and colloidal aggregates, and to assess interactions in these systems.
Equipment for spectroscopic characterisation
Fluorescence spectrophotometry
Among their numerous application in colloid and interface science, fluorescence measurements in solution permit the determination of critical aggregation concentrations.
We also have an optic fiber setup for obtaining fluorescence spectra from emission from monolayers.
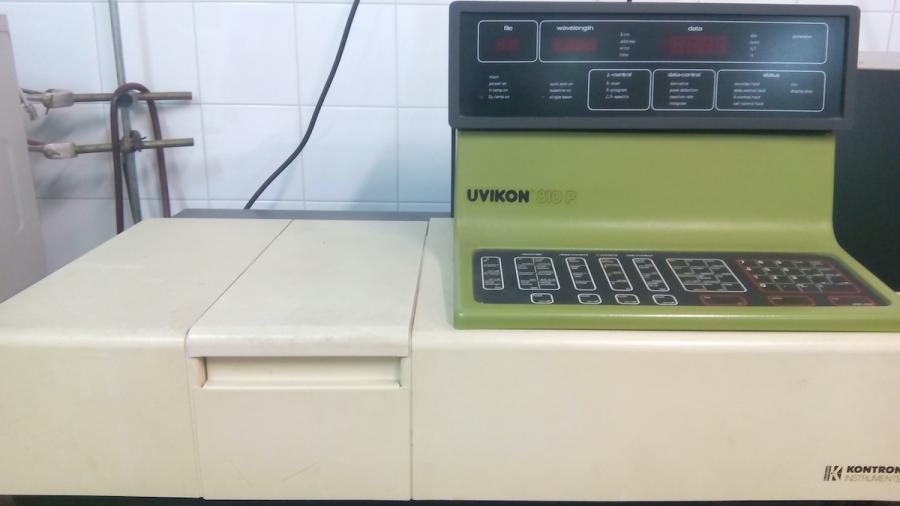
UV-visible spectrophotometry
