This paper presents relevant information to design crystalline oxides with a desired thermal conductivity and to select the appropriate substrate for applications in which heat management is important.
 The journal APL Materials recently highlighted the work titled "Analysis of the temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of insulating single crystal oxides" as "Featured Article" of its special issue on Thermoelectric Materials. This work has been led by CiQUS researcher Francisco Rivadulla, in collaboration with the Department of Physics of the University of Santiago de Compostela.
The journal APL Materials recently highlighted the work titled "Analysis of the temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of insulating single crystal oxides" as "Featured Article" of its special issue on Thermoelectric Materials. This work has been led by CiQUS researcher Francisco Rivadulla, in collaboration with the Department of Physics of the University of Santiago de Compostela.
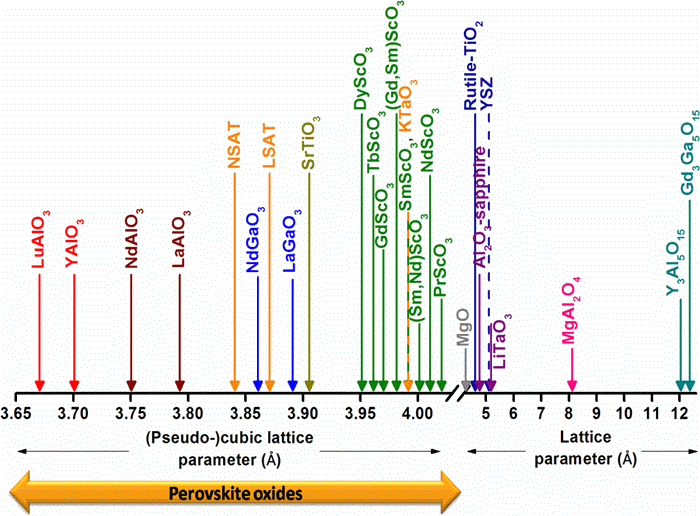
CiQUS researchers report the temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of 27 of the most common single-crystal oxide substrates used for growing epitaxial thin-film oxides, from 20 K to 350 K, covering the range of lattice parameters used to grow the vast majority of epitaxial thin films. From the analysis of these data we were able to discern between the different relevant contributions to the phonon-relaxation time in different families of oxides.
Furthermore, a detailed analysis on the basis of the Debye model suggests an important role for defect-scattering events, even in high quality single crystals. This produces very large variations of the thermal conductivity among crystals of the same family (perovskites, for instance) in spite of their similar Debye temperatures.
Particularly interesting is the huge reduction of the thermal conductivity observed in REScO3 perovskites in spite of their high crystalline quality. Their analysis proves that ≈4%-5% of vacancies at the RE-site account for this effect. Ab initio calculations suggest that this may be intrinsic to REScO3, irrespective of the method of synthesis.


